LSTM and Siamese based PitchTrainer similarity calculation
using Siamese network architecture and LSTM layers to process the input data
Abstract
Introduction
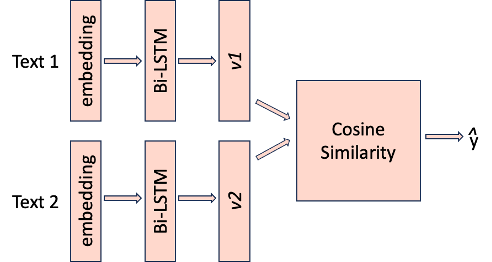
This project is a part of the PitchTrainer project. The goal of this project is to create a similarity calculation model for the PitchTrainer project. The model is based on the Siamese network architecture and uses LSTM layers to process the input data. Text similarity recognition is the key part of our project. We think that if the recognized text from Apple speech recognition API is semantic equivalent to the original text relatively, the audio can be also comprehended by a native speaker. So the problem to be addressed in this project is to use the Siamese architecture deep learning model which its two subnetworks are all LSTM layers to recognize the semantic similarities between the two texts.
Dataset
The dataset used in this project is Quora’s first public dataset regarding the problem of recognizing duplicate questions[1]. It is based on actual data from Quora helping us train and text semantic equivalence model. Our model is also focused on recognizing the similarities between the original text and the recognized text. For instance, “How can I be a good geologist?” and “What should I do to be a great geologist?” are the same questions. The total amount of samples in this dataset is over 400,000. Each sample has a duplicate question pair, ID, and a binary Integer of whether the question pair is duplicate.
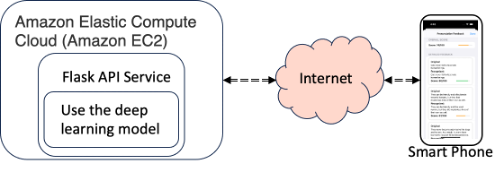
Flask API for Mobile App Integration
The app.py script establishes a Flask API server that provides endpoints for mobile applications to calculate the similarity between recognized and original texts. It utilizes the Siamese_Model.py to predict similarity scores and sentence_segmentation.py for aligning sentences before scoring.
### Usage
To start the server, run:
python3 app.py
The server listens on port 5001 and accepts POST requests to the /predict endpoint. The request body should include JSON with 'original_sentences' and 'recognized_sentences' keys. The server responds with a JSON containing the original, recognized sentences and their similarity scores.
### E.G.
request:
curl –location ‘http://hostAddress:5001/predict’
–header ‘Content-Type: application/json’
–data ‘{ “original_sentences”: “The Great Wall of China, a marvel of engineering stretching over 13,000 miles, is a series of fortifications made of stone, brick, tamped earth, wood, and other materials. “, “recognized_sentences”: “The Great Wall of China, a movie of engineering striking over 13,000 miles, is a series of fortifications made of stone, break, tamped earth, wood, and other materials.” } ‘
Response:
[ { “original”: “The Great Wall of China, a marvel of engineering stretching over 13,000 miles, is a series of fortifications made of stone, brick, tamped earth, wood, and other materials.”, “recognized”: “The Great Wall of China, a movie of engineering striking over 13,000 miles, is a series of fortifications made of stone, break, tamped earth, wood, and other materials.”, “score”: 0.855381965637207 } ]
Ensure to configure the logger as needed and check ./log/app.log for request and result logs.
## Training and Testing the model
To train the model, run the following command:
python3 training.py
or just run the training.py file in your IDE.
## Testing the model on a single custom example
To test the model, run the following command:
python3 main.py
or just run the main.py file in your IDE.
In this case, you can change the input data in the main.py file to your custom example.
## Siamese Architecture
Sub_SiameseNetwork_1( (embedding): Embedding(41708, 128) (lstm): LSTM(128, 128, batch_first=True) ) Sub_SiameseNetwork_2( (embedding): Embedding(41708, 128) (lstm): LSTM(128, 128, batch_first=True) )
## Python Notebook Version
The python notebook version of this project is available at the following folder:
./python_notebook_version/ ``` Note that the dataset path in the notebook is set to the default path. If you want to change the dataset path, you can change it in the notebook.